Is it better to do torrefaction before or after pelletisation?
Outline of the presentation
- Why torrefied biomass?
- Why to densify torrefied biomass?
- How to combine densification and torrefaction to make high quality torrefied pellets?
- Comparison of two different process pathways
—Detailed energy and mass balance
—Comparison of the wood pellet properties
- Take home messages
Torrefaction improve the biomass properties to be used as an energy/chemical commodity
- Can be co-fired efficiently with coal
—Torrefaction can enhance the calorific value closer to coal
—Torrefied particles are brittle – Easy to grind with less energy consumption
- Improves biomass properties for other applications
—Torrefied biomass based bio-oil is less acidic and more stable compared to the raw biomass
—Higher carbon content can lead to a better quality syngas production
- Easy to store
—Torrefaction can enhance the hydrophobic properties of biomass, can be stored even in an open environment
- Produce homogenous fuel
—Upgrade low quality residues and wastes
Torrefied biomass currently has some limitations
- Density of torrefied biomass is lower and challenging to transport economically over long distances
- Need to be densified for the tradability as an energy commodity
- Hard to bind during densifica1on
Why to densify torrefied biomass?
- Increase in bulk density
- Better flowability characteristics – feeding to reactors
- Predictable quality and thermal performance
But torrefied biomass particles should be densified
- With minimum energy consumption
- The resulting pellets must be stable and durable
- Must maintain the higher properties of torrefied biomass (high energy value, less susceptible to moisture ingress and mechanical damage)
How to make torrefied pellets?
- Can we densify torrefied biomass?
- Torrefied biomass is not easy to bind as the raw biomass particles
- High energy or the use of binder seems to be required to densify the torrefied biomass
- Alternatively, can we torrefy densified biomass?
- Can we maintain the physical compaction of the pellets if we torrefy them?
- Can pellets be torrefied as effective as wood chips?
One possible solution to making Torrefied pellets
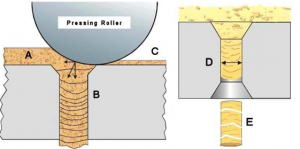
A. Pelletization Before Tarrefaction (PBT)
B. Pelletization After Torrefaction (PAT)
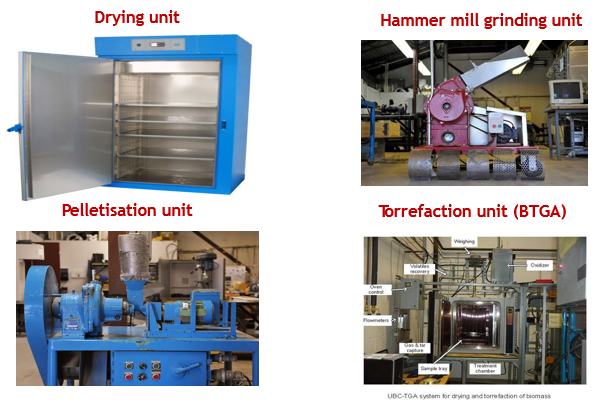
Process instruments used for the work
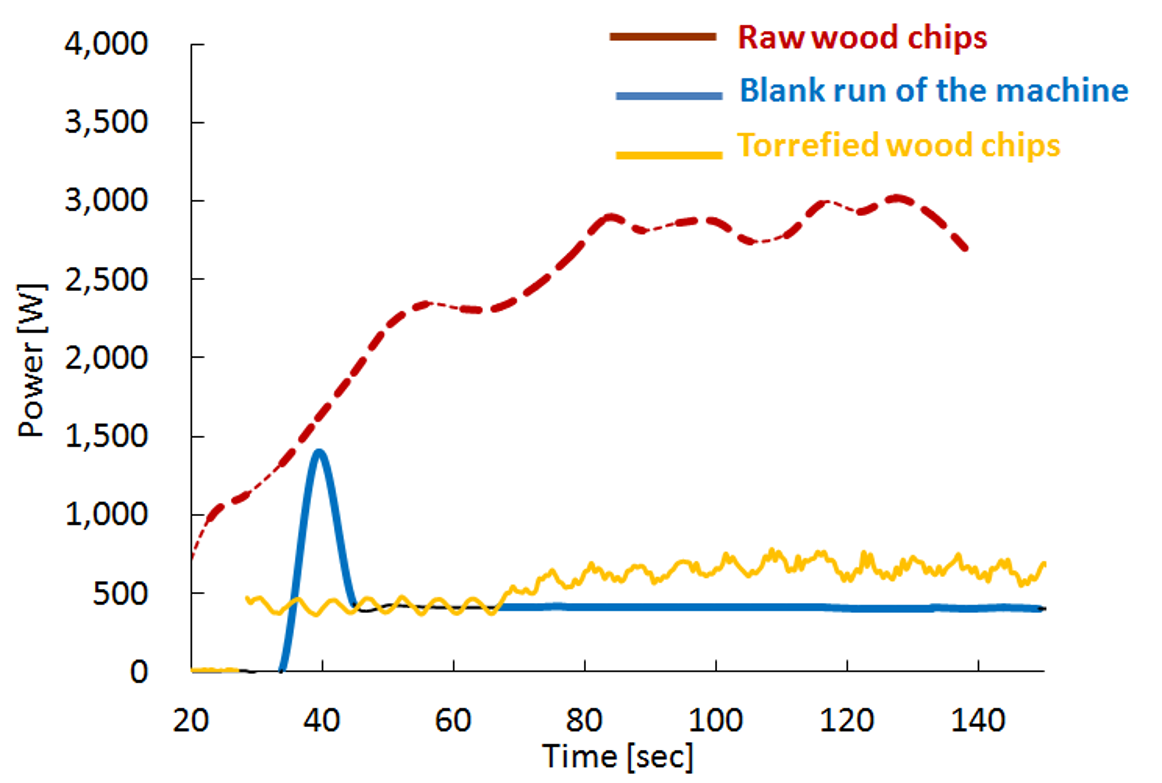
Grinding of raw wood chips vs. torrefied wood chips
Grinding of torrefied wood chips was easier compared to grinding wood chips
Grinding torrrefied material produce more fines!
Pelletizing of raw biomass vs. torrefied biomass
Pelletisation of torrefied material was energy intensive, but use of binder minimised the energy consumption
Torrefaction of raw biomass vs. pellets
Torrefaction of woodchips and regular wood pellets are fairly similar
verall energy/mass balance
Hydrophobicity of pellets: Immersing pellets in water
Physical properties of pellets made from untreated and torrefied wood chips
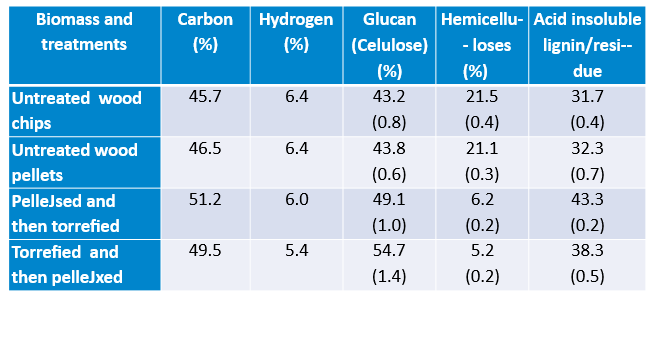
Chemical composition of the pellets made from the two pathways
Application of pathway 1 for agri-biomass torrefied pellet production
There are several concerns regarding densification of agricultural biomass
- Agri biomass has less bulk density and need more compression for pelletization
- Some agri biomass coated with waxy materials that prevent proper pelletization
- Conditioned ground agri-biomass loss moisture faster than the woody biomass
Torrefied Agri-Biomass pellet samples at 260oC for 15 minutes
Densification of raw material production of denser pellet
Effect of pretreatment
1.Steam explosion pretreatment
2.Effect of die thickness on pellet density
3.Effect of size distribution on pellet density
Steam explosion of raw materials
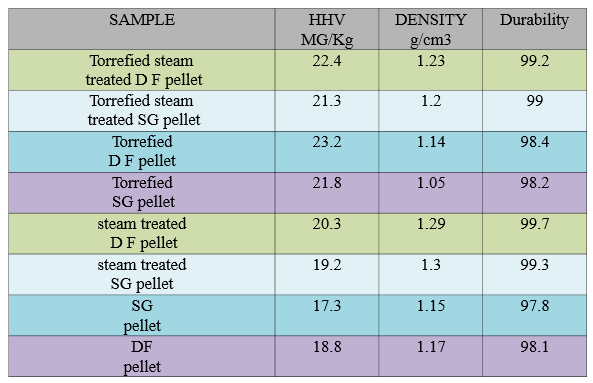
Douglas fir and Switch grass pellet quality in different stages
Effect of die thickness on pellet density